RISA-2D
will optimize
The Member Design Rules Spreadsheet records the parameters for the optimization. Optimization is performed for minimum weight, taking into consideration any depth, width, rebar limitations, etc. Note that the design rules input is one large spreadsheet, thus all of your design rules will be in the same place. Note that the dimensional rules and the reinforcement rules are all a separate entity. They have no interaction with each other in the program. They are simply all input into the same location. For example, your minimum member width rules will not be influenced by concrete beam reinforcement rules.
You can assign the design rules graphically as you draw
For additional advice on this topic, please see the RISA Tips & Tricks webpage at risa.com/post/support. Type in Search keywords: Redesign.
Note:
A Design List defines a set of member sizes that are considered when the program is suggesting member sizes. You may assign a Design List to a member based on Member Type. The design lists available for Column members may not match the design lists for Beam members, because some shapes are more appropriate for use as beams than as columns. You may edit these lists or create additional custom lists of your own. For more information on these redesign lists, including file format, editing procedure, and user defined lists refer to Appendix A - Redesign Lists.
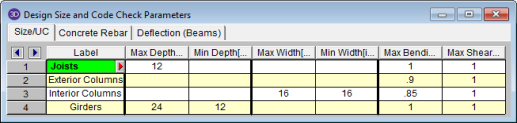
The Design Rules Spreadsheet records the limitations for the design and may be accessed by selecting Design Rules on the Spreadsheets Menu. You may create and name any number of design rules and assign different rules to various members.

The spreadsheet has three tabs: Size/UC, Deflection
You must assign a unique label to the design rules. You then refer to the design rule by its label when assigning it to members. The label column is displayed on all tabs of the spreadsheet.
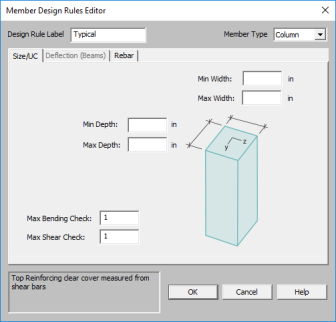
You may enforce depth restrictions by setting either a maximum and/or minimum depth.
You may enforce width restrictions by setting either a maximum and/or minimum width.
Enter the maximum bending and shear unity checks. This should usually be specified as "1". If you desire a larger factor of safety, provide a lower factor (i.e. ".95").
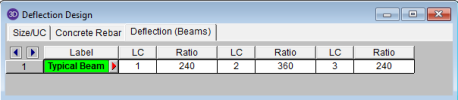
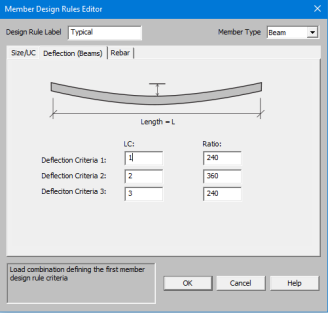
This spreadsheet allows you to define deflection criteria for beams in the model. You must choose specific load combinations from the Load Combinations spreadsheet (up to three) and give the maximum deflection L/y criteria.
Note:
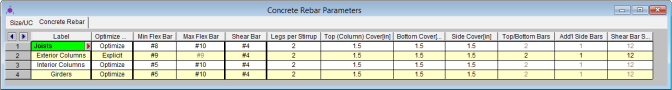
The entries for the Concrete Rebar tab are explained below.
Note
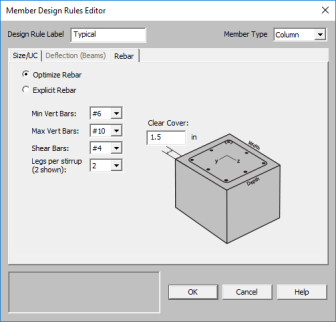
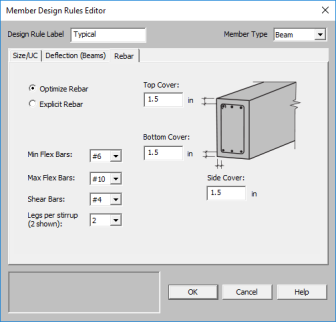
The options in this column are Optimize and Explicit. Optimize indicates the program will find the most optimal size and spacing of the reinforcement. Explicit indicates the exact number of and size of reinforcement bars. When Explicit is selected the additional columns are editable and allow you to enter the quantity for Top/Bottom Bars, Add'l Side Bars, and Shear Bar Spacing. These columns are greyed out when Optimize is selected.
Use the Min Flex Bar and Max Flex Bar columns to restrict bar sizes for your flexural reinforcing. Currently we support the ASTM A615 (imperial), ASTM A615M ("hard" metric, i.e. #8M is an 8mm bar), BS 4449 (British), prENV 10080 (Euro), CSA G30.18 (Canadian), and IS 1786 (Indian) reinforcement standards. You may specify your rebar set in the Model Settings - Concrete. You can force the program to analyze one bar size by setting the Min and Max values to be the same bar.
Use the Shear Bar column to enter the size of your shear ties. Currently we support the ASTM A615 (imperial), ASTM A615M ("hard" metric, i.e. #8M is an 8mm bar), BS 4449 (British), prENV 10080 (Euro), CSA G30.18 (Canadian), and IS 1786 (Indian) reinforcement standards. You may specify your rebar set in the Model Settings - Concrete.
Use the Legs per Stirrup column to enter the specific information about how may legs (2 to 6) each of your shear ties is expected to have.
The last three columns are used to specify the clear cover measured to the shear reinforcing. Note that the Top Cover is used for all sides of Column members.
The Member Design Rules Editor provides a way to create or modify member design rules in a graphical way. This editor automatically updates any information input into the Member Design Rules spreadsheet.
Note:
Keep in mind that this dialog has
The Design Rule Label is editable and will change the spreadsheet label. It is useful to name the design rule with a descriptive name like "First Floor Columns".
The Member Type listed is for reference of the picture only in this dialog. The member type will not control the Member Type of the beam or column which you will need to assign separately when the member is drawn.
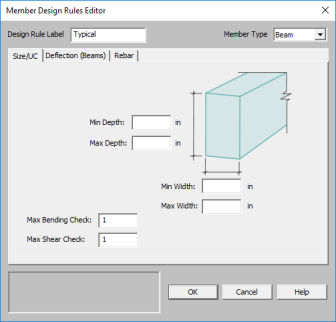
This only applies to Beam members.
You can select Optimize or Explict to set the rebar design parameters.
To access this editor you can click the
Member optimization is performed both on explicitly defined members and on members defined through the use of Section Sets. Members defined as part of a Section Set are checked to determine which member has the highest code check value and which member has the highest shear check value. These members are considered to be the controlling members for that section set.
The controlling forces on a member or a section set are then applied to new shapes satisfying the redesign parameters and a code check is calculated. If the calculated code check and shear check falls within the specified range the shape is considered to be an acceptable alternate.
Access the Member Suggested Shapes
spreadsheet by selecting the Results Menu and then selecting Members ![]() Suggested Design. Alternatively you can click the Suggested Design button on the Results floating toolbar.
Suggested Design. Alternatively you can click the Suggested Design button on the Results floating toolbar.
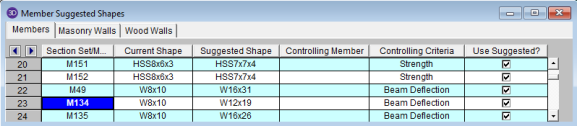
These are the suggested shapes resulting from the optimization calculations. They are chosen from each member's assigned Design List. The suggested shape is estimated to most closely meet the criteria specified in the Member Design Rules without exceeding them. If the member is a "Beam" member type then the Controlling Criteria could be based on either strength criteria or deflection criteria.
Note:
To confirm that these alternate shapes are acceptable you MUST adopt any changes into the model then re-solve and check the results. The suggested shapes are based on the forces for the current model. Keep in mind that the current results are based on the stiffness of the current shapes. Changing the shapes will change the stiffness, which is why the model needs to be resolved. It may be necessary to cycle through this process a few times to achieve the best shapes.
You may try the new shapes by clicking
the Replace and Resolve  button. The shapes listed in the Suggested Shapes column will only be used
to update the model if the "Use Suggested?" box is checked for that particular
member or section set.
button. The shapes listed in the Suggested Shapes column will only be used
to update the model if the "Use Suggested?" box is checked for that particular
member or section set.
If the message "No Shapes Found" is given, then no satisfactory shapes could be found in the Design List specified for that member or section set. This can occur for a number of reasons. Common reasons are:
Note: